In our latest OPINION post, Quality Management Tutor Manish Kumar CQP MCQI explores the role of strategic management in fostering a performance-driven culture. He examines how Tesla’s, a global leader in automotive manufacturing, commitment to a performance-driven culture has wielded significant results.
In the fast-paced and constantly evolving business world, strategic management plays a key role in leading organizations to sustainable success. A performance-driven culture that prioritizes high standards, continuous improvement and accountability is essential to achieving long-term strategic goals. This article delves into the concept of strategic management and how it cultivates a performance-driven culture, illustrated through a detailed case study of Tesla, a global leader in automotive manufacturing.
WHAT IS STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT?
Strategic management is the administration of an organization’s resources to meet its goals and objectives. Strategic management comprises of goals setting, assessment of plans, examining the internal structure, assessing the competitive landscape, developing newer strategies and making sure that management implements the plans throughout the organization. Developing strategies to achieve goals and objectives, assessing internal and external influences, and managing an organization’s resources are all part of strategic management. There are five essential stages that organizations can use to chart out their strategy.
1: Objective/Goal setting:
An organization must first set achievable, well-defined objectives so that they clearly state the organization’s goals and the rationale supporting them. The organization can identify its long- and short-term objectives at this stage.
2: Industry and organizational analyses
The following stage is for organizations to analyse, comprehend, and define how internal and external factors impact their objectives and organization, as well as what they need to do to be competitive. During this stage, analytical tools like SWOT analysis, PESTLE analysis & Porter’s 5 forces analysis are helpful.
3: Strategy framework development
Based on the results of the analysis using analytical tools, the organization can next develop the strategy on how it will accomplish the set objectives. The organization will determine in this phase how much manpower, material, machinery and other resources are required for the effective implementation of the strategies, how to assign these resources to tasks, and what performance indicators are required to determine success. Getting support from corporate leaders and other internal & external stakeholders is also essential. In business, strategic management is important because it allows the company to analyse the inherent goals affecting the activity. In many cases, organization may follow either an analytical process that identifies potential threats and opportunities, or simply follow general guidelines.
4: Strategy implementation
After finalizing the strategy, it’s time to begin implementation. During this phase, the allocated resources are placed into action based on their roles and responsibilities.
5: Measurement, monitoring, and controlling of strategies
The ultimate phase of strategic management involves evaluating the success of implemented strategies through the use of specific metrics. The organization may also consider whether ineffective strategies should be replaced by more profitable ones. The organization must continue to monitor the business environment, internal operations and maintain strategies that have proven effective.
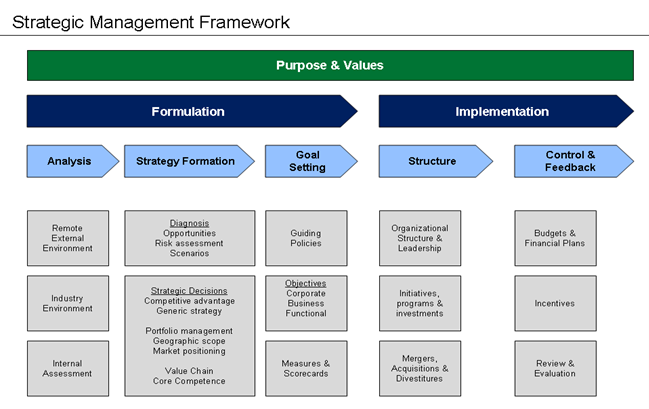
Image courtesy: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Strategic_Management_Framework.png#/media/File:Strategic_Management_Framework.png
HOW TO CULTIVATE A PERFORMANCE-DRIVEN CULTURE?
A performance-driven culture is characterized by a focus on achieving high standards of performance across all areas of the organization. It involves setting clear goals, measuring performance, and continuously seeking ways to improve. Strategic management plays a crucial role in developing this culture by:
- Aligning CI initiatives with strategic objectives
Ensuring that continual improvement initiatives support the overall strategic direction of the organization. - Engaging employees
Empowering employees to take ownership of respective KPIs and performance improvement. - Fostering innovation
Encouraging innovative solutions to enhance quality and performance. - Promoting accountability
Holding individuals and teams accountable for their contributions to the achievement of strategic objectives and performance.
CASE STUDY – TESLA, INC. STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT ANALYSIS
Tesla, Inc. is a prime example of how strategic management can cultivate a performance-driven culture.
A: BACKGROUND
Tesla Motors, Inc. is an American car manufacturer led by Elon Musk. The company marked its entry into the automotive market with the Roadster sports car, a fully battery-powered vehicle. Two engineers, Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning , founded Tesla in 2003. Eberhard looked for a sports car, but did not find- climate friendly car. He also noted that battery technology was advanced enough to make an efficient electric sports car. Tesla received several rounds of seed funding before going public. Elon Musk was their first major investor and then became CEO in 2007 – right before Tesla delivered its first commercial product the Roadster.
Under Musk, Tesla expanded beyond the automobile by establishing an entire line of alternative energy products that are highly compatible with each other. Tesla has a functional form of organizational structure that enables it to exercise strong control of the business. This structure allows Tesla to maximize its ability to implement new strategies and manage its operations. Despite maintaining regional divisions, Tesla’s emphasis on global centralization means that the entire organization is controlled by decisions made by a central group or team.
Tesla’s organization structure is one of the key factors that influences its culture. The six key characteristics of Tesla’s culture (as identified by Meyer, 2016; listed below) make Tesla a learning organization that can survive in everchanging business landscape.
CORE FEATURES OF TESLA’S ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE (MEYER, 2016)
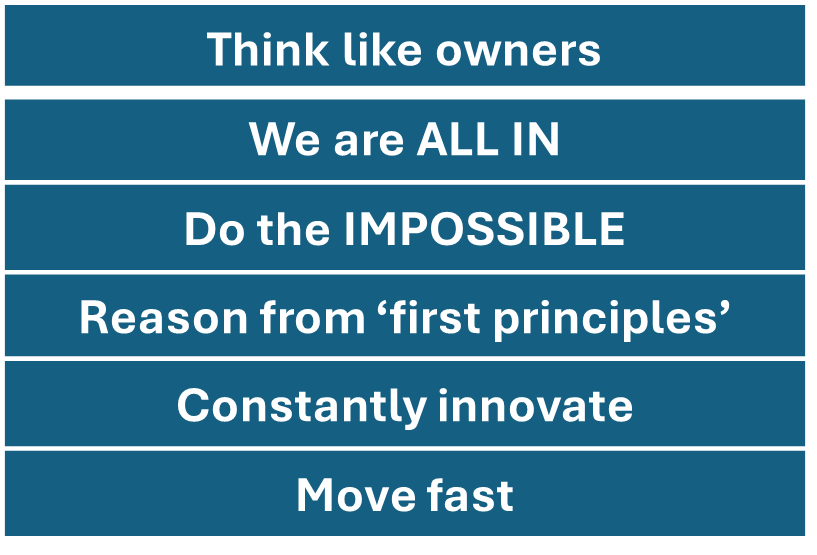
Tesla as a learning organization values individual control (“Think like owners”) and encourages employees to continuously think, develop, and innovate (“Constantly innovate”). The company strives to reward the innovative contribution of employees.
Guided by strong leadership, Tesla employees share a common vision (“Do the Impossible”) that unites them and reduces conflict.
The global scope of this vision shows bold systems thinking, and in addition, Tesla executives encourage their employees to use complex mental models (“Reasons from “first principles”) to find the root cause of problems and respond to them very quickly and effectively (“Move fast”). Tesla has training programs to guide its organizational culture. Finally, rooted in the software development culture and practices of Silicon Valley, Tesla values team learning and effective teamwork (“We are ALL IN”).
B: INNOVATION
Integrative innovation is part of the fabric of Tesla’s culture; in 2016, Forbes Magazine rated it the World’s Most Innovative Company. Tesla prioritizes design over marketing.
The strategic management practices at Tesla offer an exceptional example. Tesla is the only automobile manufacturer that sources its funds from customers before manufacturing the car. Ultimately, their decision to sell directly to customers changed the traditional dealer-based automotive supply chain. This innovation led to the development of a vehicle that can be more expensive as it ages, for the first time in the history of cars.
C: IMPACT ON PERFORMANCE-DRIVEN CULTURE
- Employee Empowerment and Engagement
Tesla’s strategic management practices empower employees at all levels to contribute to problem-solving and process improvements. This involvement fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the organization’s goals.
- Customer-Centric Approach
By prioritizing continuous improvement & innovation, Tesla ensures that customer satisfaction is at the core of its operations. This customer-centric approach is a fundamental aspect of the organization’s strategic culture.
- Sustainability and Innovation
The commitment to eliminating waste and improving efficiency not only enhances profitability but also contributes to sustainability. Tesla’s culture of continuous improvement drives innovation in products and processes.
- Alignment of Goals
Through strategic management practices, Tesla ensures that there is a clear alignment between the organisation’s strategic objectives and its operational activities. This alignment is crucial for maintaining a cohesive strategic culture.
D: RESULTS
Tesla’s commitment to a performance-driven culture has yielded significant results:
- Market Leadership: Tesla consistently ranks among the top automobile manufacturers in terms of sales, market share, and customer satisfaction.
- Innovation: The company is known for its innovative products and processes, such as hybrid technology and advanced manufacturing techniques.
- Operational Excellence: Tesla’s efficient and flexible production system is a benchmark for the industry.
E: CONCLUSION
Cultivating a performance-driven culture requires a holistic approach. It’s not just about processes; it’s about fostering a collective commitment to achieve strategic objectives.
Tesla’s case demonstrates how integrating strategic management principles with strategic objectives can lead to sustained success and a strong organizational culture. By adopting similar practices, organizations can enhance their strategic alignment, foster innovation, and achieve long-term excellence.
Manish Kumar CQP MCQI
Quality Management Tutor, rove.
If you’re interested in studying one of our CQI and IRCA Quality Management courses, you can find out more here.

